Redux Simplified: A Beginner's Guide for Web Developers
Table of Contents
Hi there👋,
In this post you will learn the simple concept behid the Redux in simpler terms so make sure to read the whole article. If you prefer to watch video then here it is else you can keep reading 😄!
Before going into what is Redux? Let’s see why we needed Redux in the first place. Now let’s dive in ^_^.
The Problem
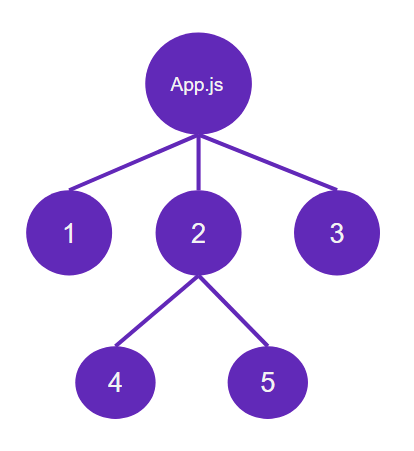
Let’s say as a root component you have App.js file in your project, and in the component tree, the first layer contains 3 components and in the 2nd layer there are two child component of 2nd parent component.
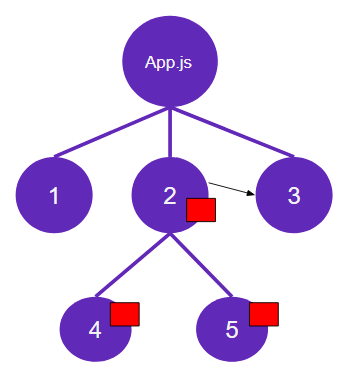
Here, you have fetched the data from an API and you save it in the state of 2nd component. You can use this data state in child components by directly passing them downwards. Now, the problem occurs when the neighbor component which is 3 want to access that data state.
So the problem is when multiple components that need to share and use the same state.
This can be solved by lifting up the state to the parent component. So you can lift state from 2nd component to the App.js file and then you can use this state in the 3rd component. But that does not help always because in large application there are many states needed to be used in many different components, so it is not the best practice.
One way to solve this problem is to take state outside of the component tree and set it as centralized. So that any component in the tree can access and update the state without worrying about it’s hierarchy in the tree. This is the basic idea behind Redux: A single centralized place to contain the global state in your application, and specific patterns to follow when updating that state.
You can use Redux to store the state then you can use that state to any component without worrying about the hierarchy.
How Application Works in React
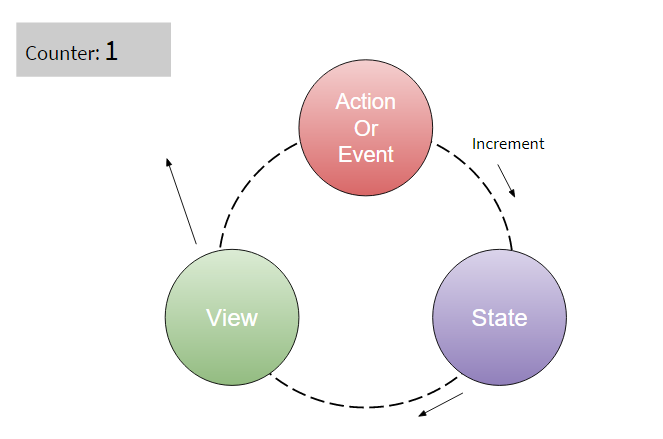
Consider the action as a trigger to update the state and when state gets changed then view updates the UI with new state. For simple counter application, when we increment counter value then increment event goes to state and state updates new value then, view re-renders ui based on the updated state. So let’s see what happens when you use Redux.
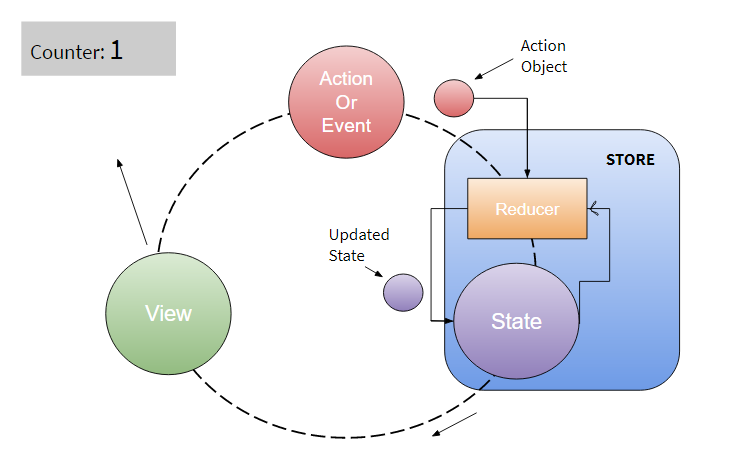
In the Redux there is a function called reducer . This reducer function takes two arguments, first is the state itself, and second is the action object. An action object can have a type of action like increment and any data that wants to modify the state.
store , you can say the store is like a centralized database for state management. When view get new state value it re-renders the UI. Let me show you another example of how redux works!
As you can see here this is a simple gif which explains how redux works, you can find it on the official redux documentation. Now using this UI you can either deposit or withdraw money. When we click the deposit button, click event goes to event handler, based on event the event handler dispatches an action with the type as deposit and any details needed in the payload property.
This reducer accepts two things, state and the action object . Previous value of state is 0$ and action is for deposit, so the reducer will update the new state by depositing 10$ amount. You can see in the UI balance, it changed from 0 to 10$.
Redux by definition
It is a Predictable State Container for JS Apps. It is,
Predictable: because it helps you write applications that behave consistently, and can run in different environments (client, server, and native).
Centralized: because of this feature, we don’t need to lift state to parent components and we can use state from any component we want due to this centralized behavior.
Debuggable: There is an extension called Redux DevTools which is an excellent tool to debug Redux applications. Using this tool you can see when, where, why, and how your application’s state changed.
Flexible: because it works with any UI layer, and has a large ecosystem of addons.
That concludes this post. I trust you gained some valuable insights from this blog.